Welcome my dear Philippine literature learners! This is our next lesson in Philippine literature course, the Divisions of Literature. After knowing what is literature, its definition, the Literary Standards, the Literary Approaches as well as Importance of Literature, now is the right time to study and learn about the Divisions of Literature and the colorful Literary Genres. I enjoin you to make use of this web site as an extension of our four-walled classroom and very limited class contact hours. Although I take a considerable effort in maximizing this web page, still, I require you to attend personally our classes regularly. No amount of web presence can substitute our genuine class interaction. Besides, it is required that you complete our required number of contact hours. This i just an extension of our normal yet limited class contact hours. It is never my intention to let you forego nor miss our classes, but this effort is meant to support and augment our sessions that’s why I set this website up.
“Literature adds to reality, it does not simply describe it. It enriches the necessary competencies that daily life requires and provides; and in this respect, it irrigates the deserts that our lives have already become.” ~ C.S. Lewis
Intended learning outcomes (ILOs)
By the end of this lesson, you are expected to:
- Enumerate and distinguish the different literary genres;
- Cite example of each literary work and its classification.
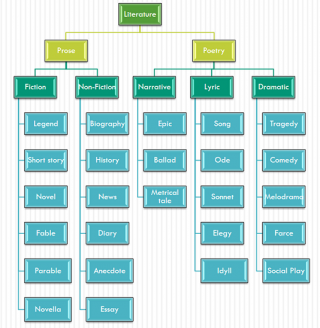
Divisions of Literature
Literary works involve written and oral accounts of humanity’s existence. In the Philippines, locally, it is a collection of various written and oral depiction of how the lives of these local inhabitants unfold. Hence we have such things as Ilokano Literatures, Bikol Literatures, Waray Literatures, Maranao Literatures, among others. Hence, the vast collections of these works from the local scale up to global scale make it tedious and cumbersome to study and analyze.
To understand these works better, we need to look at them by studying the Divisions of Literature. Gleaning from the image above, we can see the various divisions and the corresponding Literary Genres.
A. Prose is a division of literature which covers a literary work that is spoken or written within the common flow of language in sentences and in paragraphs which gives information, relate events, express ideas, or present opinions. Under this division, we have two sub-divisions: the Fiction and Non-Fiction.
- Fiction is a sub-division of prose which covers a literary work of imaginative narration, either oral or written, fashioned to entertain and to make readers think and more so, to feel. It normally came from the writer’s imagination. Some Literary Genres that fall under fiction include:
- Legend is a prose fiction which attempts to explain the origin of things, places, objects that we see around us. Example: The Legend of Makahiya, Why the Sea is Salty.
- Short story is a short prose fiction narrative depicting a simple characterization and plot conveying a moral which can be read in one sitting. Example: The Diamond Necklace by Guy de Maupassant, Footnote to Youth by Jose Garcia-Villa.
- Novel is a very long prose narrative depicting complex characterization and plot which is usually divided into chapters. Example: Les Miserables by Victor Hugo, War and Peace by Leo Tolstoy.
- Novella is a long prose narrative similar to but shorter than a novel but longer than a short story. It is also known as novelette. Example: Treasure Island by Robert Louis Stevenson, The Call of the Wild by Jack London.
- Fable is a short prose fiction narrative depicting animal characters which espouses a lesson in life. Example: The Lion and the Mouse, The Monkey and the Turtle.
- Parable is a short prose allegorical narrative which presents a philosophical outlook in life. Example: The Parable of the Sower, The Prodigal Son.
- Legend is a prose fiction which attempts to explain the origin of things, places, objects that we see around us. Example: The Legend of Makahiya, Why the Sea is Salty.
- Non-Fiction is a sub-division of prose which covers a literary work of “real life” narration or exposition based on history and facts whose main thrust is intellectual appeal to convey facts, theories, generalizations, or concepts about a particular topic. Some literary genres that fall under non-fiction include:
- Biography is a prose non-fiction detailing the life of a person written by another person. Example: The Great Malayan about the Life of Jose Rizal written by Carlos Quirino. Sometimes, a biography may be written by the same person, hence, it is called autobiography. Example: Memoirs written by Juan Ponce Enrile was a lengthy narrative about his own life.
- History is a prose non-fiction record of events that transpired in the past. Example: The History of Filipino People written by Gregorio Zaide.
- News is a prose non-fiction narrative of events that happen everyday. The newspapers are written for this purpose. Example: Philippine Daily Inquirer.
- Diary is a personal account of significant events that happen in the life of a person.
- Anecdote is a prose non-fiction narrative that depicts a single incident in a person’s life. Example: The Moth and the Lamp.
- Essay is prose non-fiction which is a formal treatment of an issue written from the writer’s personal point of view. Example: On the Indolence of the Filipinos written by Jose Rizal.
- Biography is a prose non-fiction detailing the life of a person written by another person. Example: The Great Malayan about the Life of Jose Rizal written by Carlos Quirino. Sometimes, a biography may be written by the same person, hence, it is called autobiography. Example: Memoirs written by Juan Ponce Enrile was a lengthy narrative about his own life.
B. Poetry is a division of literature works which covers a literary work expressed in verse, measure, rhythm, sound, and imaginative language and creates an emotional response to an experience, feeling or fact. Traditionally, it has three sub-divisions namely: Narrative poetry, Lyric poetry, and Dramatic poetry.
- Narrative Poetry is a sub-division of poetry which tells or narrates a story. It may be lengthy as an epic, or short as a ballad and typically measured as a metrical tale.
- Epic is a narrative poem which accounts the heroic exploits of a community’s hero, usually involving superhuman abilities. Example: Hudhod hi Aliguyon is an Ifugao epic.
- Ballad is a narrative poem which depicts a single incident that transpired in a person’s life. It is usually recited during gatherings in the past but it may be sung in the present days. Example: Forevermore by Side A Band.
- Metrical Tale is a narrative poem which narrates a story in a “metered” or “measured” number of syllables hence it was called metrical. There are two popular variations in Philippine Literature, the Awit and Corrido.
- Awit is a romance metrical tale of dodecasyllabic measure which is recited during formal performances or informal gatherings. Example: Florante at Laura by Francisco “Balagtas” Baltazar.
- Corrido is a martial or adventure metrical tale of octosyllabic measure which is recited for recreational purposes. Example: Ibong Adarna by Jose Corazon dela Cruz.
- Lyric Poetry is a sub-division of poetry which features poems intended to be sung with the accompaniment of the musical instrument called “lyre” hence, lyric poetry. The following are the types of lyric poems.
- Song is a lyric poem of various theme which is meant to be sung in its entirety. Example: Bayan Ko written by Jose De Jesus, arranged by Constancio De Guzman, and sung by Freddie Aguilar.
- Ode is a lyric poem of noble and exalted emotion which has dignified countenance. Example: Ode to the West Wind by Percy Bysshe Shelley.
- Elegy is a lyric poem of sad theme such lamentation for the dead, longing for a missing love, and a grief for things beyond one’s control. Example: Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard by Thomas Gray.
- Sonnet is a lyric poem of 14 iambic pentameter lines usually about love and beautiful themes. Example: Sonnet to Laura by Francesco Petrarch.
- Idyll is a lyric poem celebrating the tranquil and beautiful landscapes of rural and country settings. Example: Beside the Pasig River by Jose Rizal.
- Dramatic Poetry is a sub-division of poetry which features poems meant to be performed on stage. Theater plays and dramatic presentations belong to this type.
- Tragedy is a dramatic poetry which features a hero whose hubris or shortcoming eventually causes his downfall or defeat often ending in a very sad conclusion. Example: Hamlet by William Shakespeare and The Three Rats by Wilfrido Ma. Guerero.
- Comedy is a dramatic poetry which is similar with tragedy except that the hero triumphs and overcomes the odds towards the end and emerges victoriously. Example: The Twelfth Night by William Shakespeare.
- Melodrama is a dramatic poetry which is a combination of the elements of tragedy and comedy yet ends in a happy note. Example: A Midsummer Night’s Dream by William Shakespeare
- Farce is a dramatic poetry which is an exaggerated comedy that aims to elicit laughter hence, relaxation. Examples: Importance of Being Earnest by Oscar Wilde.
- Social Play is a dramatic poetry which tackles social issues and problems such as poverty, corruption, discrimination, racism, sexism, among others, with an aim to bring awareness and bring about positive change. Example: Zsazsa Zaturnah by Carlo Vergara.
- Tragedy is a dramatic poetry which features a hero whose hubris or shortcoming eventually causes his downfall or defeat often ending in a very sad conclusion. Example: Hamlet by William Shakespeare and The Three Rats by Wilfrido Ma. Guerero.
Thanks! kac po assignment po namin toh…